Lately here at XDA we have been writing a number of tutorials to show you how to access certain features of the Android platform that simply are not visible to the user. These have generally been done with the help of some command line Android Debug Bridge (ADB) commands, a tool that Google offers for developers to debug various parts of their applications or the system, but which we can use for all kinds of neat and hidden tricks. Using the command line isn’t something that everyone is comfortable with, though, so in an attempt to teach everyone how to do these tweaks (no matter what skill level you’re at), we have been including some basic steps about how to install ADB in each of our tutorials where necessary.
Method 3: Steps to Install Android ADB & Fastboot Drivers on Mac OS X: Step 1: Downloading and Extracting ADB Scripts for Mac OS. First, you need to download the necessary ADB installation Scripts for Mac OS X. Once you downloaded the Zip file then extract the file to a folder using Archive manager. The Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is a versatile command line tool that lets you communicate with and control an Android-powered device over a. Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is a command-line utility for running and managing Android apps on your device or emulator. ADB is available when you install Android Studio. If you are not using Android Studio, you need to install Android platform tools, which includes ADB.
Well, the number of our tutorials has ballooned in quantity lately, so we have decided to exclude those steps from future tutorials to avoid redundancy. However, we still want all future tutorials we write to be easy to understand for as many people as possible, so that will be the point of today’s guide. Having a dedicated step by step tutorial on how to install and setup ADB on your computer (no matter what operating system you use) will be great for those who may not have it set up already.
This will also let us include a link to this guide in the future tutorials we write that require you to have ADB setup and installed on your computer. So when one of our new tutorials comes out that requires ADB, you can click through the link to learn how to install ADB or you can simply ignore it and move onto the next step. Since ADB can be used on a variety of operating systems, we’ll be covering some basic instructions for Windows, macOS and Linux.
How to Setup the Android Debug Bridge (ADB)
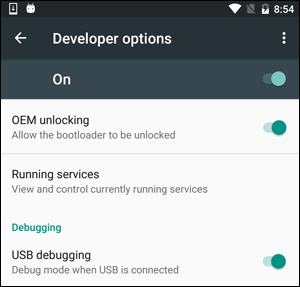
Note: Setting up ADB on the computer is just half the equation since you’ll also need to do some things on the smartphone or tablet to accept the ADB commands.
Phone Setup
- Launch the Settings application on your phone.
- Tap the About Phone option generally near the bottom of the list (this is hidden behind the “System” option in Google’s latest Android Oreo version).
- Then tap the Build Number option 7 times to enable Developer Mode. You will see a toast message when it is done.
- Now go back to the main Settings screen and you should see a new Developer Options menu you can access.
- Go in there and enable the USB Debugging mode option.
- You are partially done with the phone setup process. Next up, you will need to scroll below and follow the rest of the instructions for your particular operating system.
Microsoft Windows ADB Setup
- Extract the contents of this ZIP file into an easily accessible folder (such as C:adb)
- Open Windows explorer and browse to where you extracted the contents of this ZIP file
- Then open up a Command Prompt from the same directory as this ADB binary. This can be done by holding Shift and Right-clicking within the folder then click the “open command prompt here” option. (Some Windows 10 users may see “PowerShell” instead of “command prompt”.)
- Connect your smartphone or tablet to your computer with a USB cable. Change the USB mode to “file transfer (MTP)” mode. Some OEMs may or may not require this, but it’s best to just leave it in this mode for general compatibility.
- In the Command Prompt window, enter the following command to launch the ADB daemon:
adb devices - On your phone’s screen, you should see a prompt to allow or deny USB Debugging access. Naturally, you will want to grant USB Debugging access when prompted (and tap the always allow check box if you never want to see that prompt again).
- Finally, re-enter the command from step #6. If everything was successful, you should now see your device’s serial number in the command prompt. Yay! You can now run any ADB command on your device! Now go forth and start modding your phone by following our extensive list of tutorials!
How to Install ADB on macOS
- Extract the ZIP to an easily-accessible location (like the Desktop for example).
- Open Terminal.
- To browse to the folder you extracted ADB into, enter the following command:
cd /path/to/extracted/folder/ - For example, on my Mac it was this:
cd /Users/Doug/Desktop/platform-tools/ - Connect your device to your Mac with a compatible USB cable. Change the USB connection mode to “file transfer (MTP)” mode. This is not always required for every device, but it’s best to just leave it in this mode so you don’t run into any issues.
- Once the Terminal is in the same folder your ADB tools are in, you can execute the following command to launch the ADB daemon:
adb devices - On your device, you’ll see an “Allow USB debugging” prompt. Allow the connection.
- Finally, re-enter the command from step #7. If everything was successful, you should now see your device’s serial number in macOS’s Terminal window. Congratulations! You can now run any ADB command on your device! Now go forth and start modding your phone by following our extensive list of tutorials!
How to Install ADB on Linux
- Extract the ZIP to an easily-accessible location (like the Desktop for example).
- Open a Terminal window.
- Enter the following command:
cd /path/to/extracted/folder/ - This will change the directory to where you extracted the ADB files.
- So for example:
cd /Users/Doug/Desktop/platform-tools/ - Connect your device to your Linux machine with your USB cable. Change the connection mode to “file transfer (MTP)” mode. This is not always necessary for every device, but it’s recommended so you don’t run into any issues.
- Once the Terminal is in the same folder your ADB tools are in, you can execute the following command to launch the ADB daemon:
adb devices - Back on your smartphone or tablet device, you’ll see a prompt asking you to allow USB debugging. Go ahead and grant it.
- Finally, re-enter the command from step #8. If everything was successful, you should now see your device’s serial number in the Terminal window output. Congrats! You can now run any ADB command on your device! Now go forth and start modding your phone by following our extensive list of tutorials!
Some Linux users should be aware that there can be an easier way to install ADB on their computer. The guide above will certainly work for you, but those own a Debian or Fedora/SUSE-based distro of Linux can skip steps 1 and 2 of the guide above and use one of the following commands. . .
- Debian-based Linux users can type the following command to install ADB:
sudo apt-get install adb - Fedora/SUSE-based Linux users can type the following command to install ADB:
sudo yum install android-tools
Just to cover all of our bases here, Linux users may need to put a ./ in front of the ADB commands we list in future tutorials. This is something that is likely known by any Linux user already, but again, we want as many people as possible to understand how to do these tweaks for Android no matter how much of your operating system you know.
Adb Drivers Samsung
Bonus: For those who want to take this a step further, you can follow this new tutorial we put together that will walk you through how to setup ADB so that you can use the command from any directory on a Windows or Linux desktop.
Discuss This StoryAdb Fast Boot Drivers

Mac Android Adb
Want more posts like this delivered to your inbox? Enter your email to be subscribed to our newsletter.